In even the most developed European countries, there are big gaps in internet access. Around 50 % of rural households had no broadband access in 2017 due to the challenges service providers encounter in those areas. Unlike urban regions, rural areas have a varying degree of terrain, making executing a cable or fiber buildout difficult and costly. Luckily, there might already be an inexpensive solution available: television white space stands to transform the way we purchase and use wireless internet. However, this disruptive technology isn’t yet widely adopted.
White space is the name given to unused broadcasting frequencies in the wireless spectrum. Television networks leave gaps between channels for buffering purposes, and this space can be used to deliver broadband internet. The signal can travel up to 10 kilometres and difficult terrain like hills. Rural areas are often inhibited from wireless access because they are inaccessible 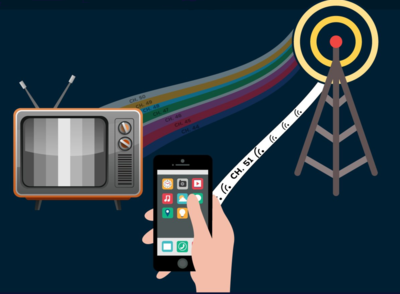 and sometimes off the local power grid. Nevertheless, agricultural activities make up the basic fabric of rural life, contributing significantly to the overall state of rural areas in terms of employment and business opportunities. The concept of rural development must therefore be considered with particular reference to agriculture. Fortunately, white space stations can be charged with solar panels as they only require a very limited amount of electricity. With the next generation of wireless technology, known as 5G, just around the corner, such innovative approaches for ensuring affordable connectivity in hard-to-reach rural areas are crucial for the future.
and sometimes off the local power grid. Nevertheless, agricultural activities make up the basic fabric of rural life, contributing significantly to the overall state of rural areas in terms of employment and business opportunities. The concept of rural development must therefore be considered with particular reference to agriculture. Fortunately, white space stations can be charged with solar panels as they only require a very limited amount of electricity. With the next generation of wireless technology, known as 5G, just around the corner, such innovative approaches for ensuring affordable connectivity in hard-to-reach rural areas are crucial for the future.
According to Microsoft, which intends to leverage TV white space (TVWS) for sensor operations, the viability of the technology has been proven in more than a dozen trials around the world, ranging from remote villages in Africa to dense urban centres in Asia. Thus, it can be used for precision agriculture applications, such as monitoring soil moisture level, remote diagnostics or autonomous vehicles. The connection of data brought through wireless broadband connectivity empowers farmers to make more timely and better-informed decisions about their harvests and better support their livelihoods.
The white space devices currently in use do not serve tablets or laptops, but they provide a link to a receiver that is connected to a regular internet hub. This makes the solution go where broadband has never gone before: connecting the unconnected. White space is perfect to provide broadband connectivity to rural communicates and also to connect IoT devices in urban areas. This unlicensed, free form of broadband is gaining traction and stands to transform the way we use wireless internet.